

getParts(): returns a collection of Part objects.New methods introduced in HttpServletRequest interface:.The file is created relative to the location specified in the MultipartConfig annotation. write(String filename): this is the convenience method to save upload data to file on disk.getSize(): returns the size of upload data, in bytes.getInputStream(): returns an InputStream object which can be used to read content of the part.This interface defines some methods for working with upload data (to name a few): Interface Part : represents a part in a multipart/form-data request.maxRequestSize :maximum size for a request.maxFileSize : maximum size for a single upload file.location : directory where file will be stored via Part.write() method.fileSizeThreshold : file’s size that is greater than this threshold will be directly written to disk, instead of saving in memory.The MultipartConfig annotation has the following options: Annotation : A servlet can be annotated with this annotation in order to handle multipart/form-data requests which contain file upload data.File Upload API in Servlet 3.0The Servlet 3.0 API provides some new APIs for working with upload data: Of course you can use newer versions of Java EE and Tomcat server. Fortunately, developers do no longer have to depend on any external library, since Java EE 6 provides built-in file upload API.Runtime requirement:
#Java applet file upload example code code#
The code of the HTML form is as = " FileUploadServletExample ", urlPatterns = class FileUploadServletExample extends HttpServlet ", partHeader) įor (String content : part.getHeader("content-disposition").Before Java EE 6, applications usually have to use an external library like Apache’s Common File Upload to handle file upload functionality. The data is posted to the servlet, and it stores the File to the specified location when we click on the Upload button. The destination defines the path of the location where we need to save the File in the system. The servlet handles the POST request, process the incoming file data, and extract File from the stream. With this restriction, the request sends to the server in the encoded form. We add two restrictions to the form, i.e., encrypt="multipart/form-data" and method="POST". After selecting the File from the system, we send the File as a POST request to the server. The input field of type File allows the user to browse the File from the system. We implement a Simple HTML form having two fields, i.e., File and Destination.
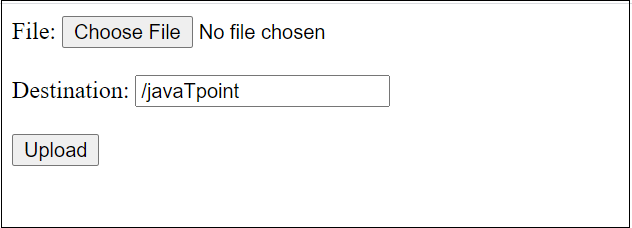
In Java, we use a single servlet and an HTML form for creating a file upload request to the servlet.
#Java applet file upload example code how to#
In this section, we will learn about how we can implement the file upload functionality in Java and will also understand how to upload a file to a folder. In order to work with File, every developer should have knowledge of how we can implement the file upload functionality in Java or other programming languages. The File plays a vital role in each programming language. Next → ← prev Java File Upload to a Folder


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
